Lifecycle
For complete understanding of the in-app purchase lifecycle, flow diagrams, and state management, please visit:
Lifecycle Documentation - openiap.dev
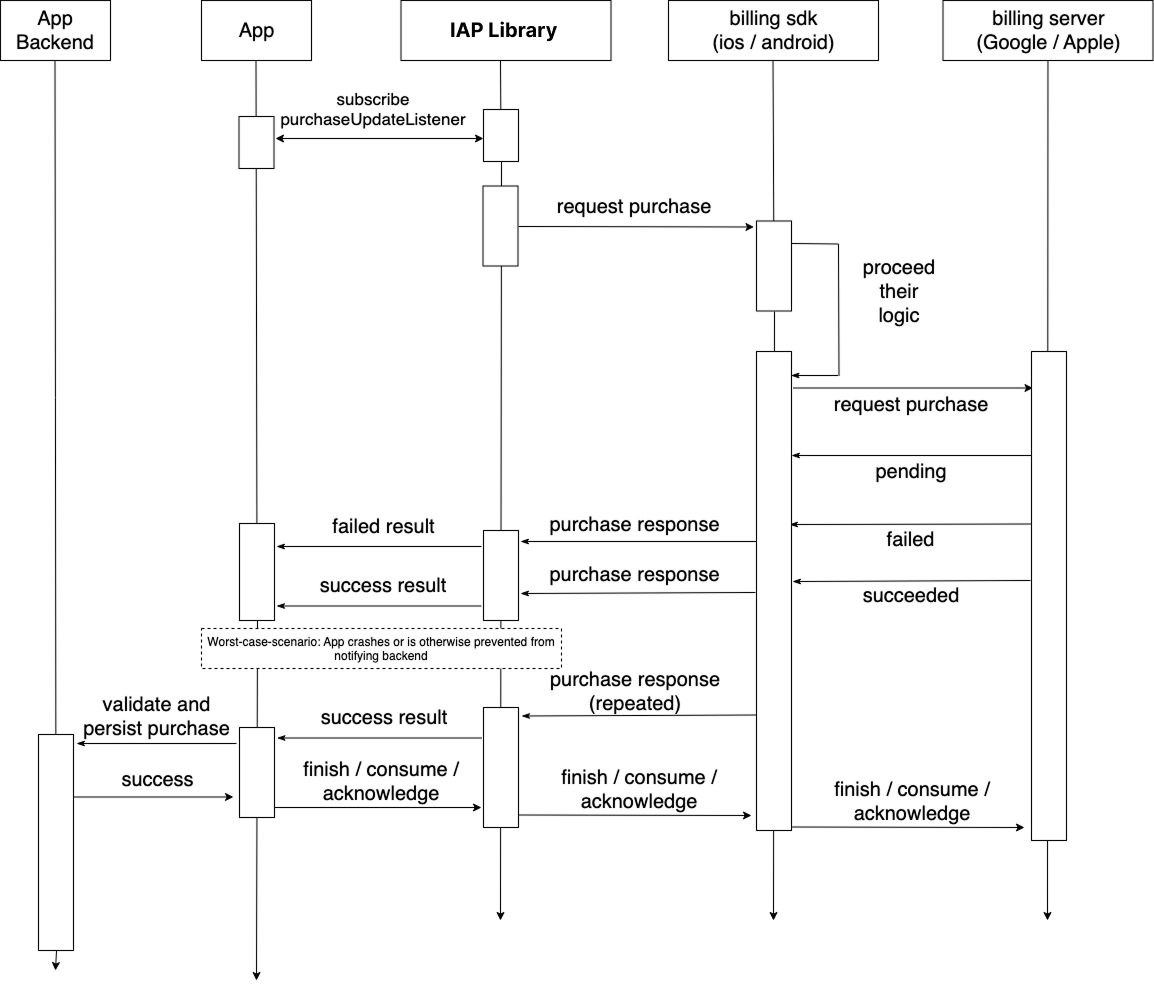
The Open IAP specification provides detailed documentation on:
- Complete purchase flow
- State transitions and management
- Connection lifecycle
- Error recovery patterns
- Platform-specific considerations
Implementation with GodotIap
Connection Management
Understanding the connection lifecycle is crucial for reliable IAP implementation.
Connection States
The connection can be in several states:
- Disconnected: Initial state, no connection to store
- Connecting: Attempting to establish connection
- Connected: Successfully connected, ready for operations
- Error: Connection failed
Basic Connection Flow
extends Node
const Types = preload("res://addons/godot-iap/types.gd")
@onready var iap = $GodotIapWrapper
var is_connected: bool = false
func _ready():
_setup_signals()
_initialize_connection()
func _setup_signals():
iap.purchase_updated.connect(_on_purchase_updated)
iap.purchase_error.connect(_on_purchase_error)
iap.products_fetched.connect(_on_products_fetched)
iap.connected.connect(_on_connected)
func _initialize_connection():
# Returns bool - true if connection successful
is_connected = iap.init_connection()
if is_connected:
print("Connected to store")
_load_products()
else:
print("Failed to connect")
_on_connection_failed()
func _load_products():
if is_connected:
var request = Types.ProductRequest.new()
var skus: Array[String] = ["coins_100", "premium"]
request.skus = skus
request.type = Types.ProductQueryType.ALL
var products = iap.fetch_products(request)
for product in products:
print("Product: ", product.id, " - ", product.display_price)
func _on_connected():
is_connected = true
print("Store connected")
Handling Connection States
var connection_error: String = ""
func _initialize_connection():
is_connected = iap.init_connection()
if is_connected:
connection_error = ""
_on_connected_successfully()
else:
is_connected = false
connection_error = "Failed to connect to store"
_on_connection_failed()
func _on_connected_successfully():
print("Store connected, loading products...")
_load_products()
func _on_connection_failed():
print("Connection failed: ", connection_error)
# Show retry UI to user
show_retry_button()
func retry_connection():
print("Retrying connection...")
_initialize_connection()
Component Lifecycle Integration
Scene Lifecycle
extends Node
const Types = preload("res://addons/godot-iap/types.gd")
@onready var iap = $GodotIapWrapper
func _ready():
# Initialize IAP when scene loads
_setup_signals()
_initialize()
func _exit_tree():
# Clean up when scene is removed
if iap:
# Disconnect signals if needed
if iap.purchase_updated.is_connected(_on_purchase_updated):
iap.purchase_updated.disconnect(_on_purchase_updated)
if iap.purchase_error.is_connected(_on_purchase_error):
iap.purchase_error.disconnect(_on_purchase_error)
# End connection
iap.end_connection()
func _setup_signals():
iap.purchase_updated.connect(_on_purchase_updated)
iap.purchase_error.connect(_on_purchase_error)
iap.products_fetched.connect(_on_products_fetched)
iap.connected.connect(_on_connected)
func _initialize():
if iap.init_connection():
_load_products()
func _on_connected():
print("Store connected")
func _on_purchase_updated(purchase: Dictionary):
# Handle purchase updates
pass
func _on_purchase_error(error: Dictionary):
# Handle purchase errors
pass
func _on_products_fetched(result: Dictionary):
# Handle fetched products
pass
func _load_products():
var request = Types.ProductRequest.new()
var skus: Array[String] = ["coins_100", "premium"]
request.skus = skus
request.type = Types.ProductQueryType.ALL
iap.fetch_products(request)
Autoload Pattern (Recommended)
For persistent IAP management, use an Autoload singleton:
# iap_manager.gd - Add this as an Autoload
extends Node
const Types = preload("res://addons/godot-iap/types.gd")
@onready var iap = $GodotIapWrapper
var is_connected: bool = false
var products: Array = []
var subscriptions: Array = []
signal iap_connected
signal iap_disconnected
signal iap_error(error: Dictionary)
signal products_loaded(products: Array)
signal purchase_completed(purchase: Dictionary)
signal purchase_failed(error: Dictionary)
func _ready():
# Note: In Autoload, $GodotIapWrapper must be added as a child node
# Alternatively, create the node dynamically:
_setup_iap_node()
_setup_signals()
_initialize()
func _setup_iap_node():
# If using Autoload, you need to add GodotIapWrapper as a child
var wrapper = preload("res://addons/godot-iap/godot_iap.gd").new()
wrapper.name = "GodotIapWrapper"
add_child(wrapper)
iap = wrapper
func _setup_signals():
iap.purchase_updated.connect(_on_purchase_updated)
iap.purchase_error.connect(_on_purchase_error)
iap.products_fetched.connect(_on_products_fetched)
iap.connected.connect(_on_connected)
iap.disconnected.connect(_on_disconnected)
func _initialize():
is_connected = iap.init_connection()
if is_connected:
iap_connected.emit()
func _on_connected():
is_connected = true
iap_connected.emit()
func _on_disconnected():
is_connected = false
iap_disconnected.emit()
func _on_purchase_updated(purchase: Dictionary):
purchase_completed.emit(purchase)
func _on_purchase_error(error: Dictionary):
purchase_failed.emit(error)
func _on_products_fetched(result: Dictionary):
if result.has("products"):
products = result["products"]
products_loaded.emit(products)
# Public API
func load_products(product_ids: Array[String]):
if is_connected:
var request = Types.ProductRequest.new()
request.skus = product_ids
request.type = Types.ProductQueryType.ALL
products = iap.fetch_products(request)
products_loaded.emit(products)
func load_subscriptions(sub_ids: Array[String]):
if is_connected:
var request = Types.ProductRequest.new()
request.skus = sub_ids
request.type = Types.ProductQueryType.SUBS
subscriptions = iap.fetch_products(request)
func buy(product_id: String, type: Types.ProductQueryType = Types.ProductQueryType.IN_APP):
if not is_connected:
return
var props = Types.RequestPurchaseProps.new()
props.request = Types.RequestPurchasePropsByPlatforms.new()
props.type = type
props.request.google = Types.RequestPurchaseAndroidProps.new()
var skus: Array[String] = [product_id]
props.request.google.skus = skus
props.request.apple = Types.RequestPurchaseIOSProps.new()
props.request.apple.sku = product_id
iap.request_purchase(props)
func restore() -> Array:
if is_connected:
return iap.get_available_purchases()
return []
Usage in other scenes:
# In any scene
extends Control
func _ready():
# Connect to the autoload signals
IapManager.products_loaded.connect(_on_products_loaded)
IapManager.purchase_completed.connect(_on_purchase_completed)
# Wait for connection
if IapManager.is_connected:
_load_store()
else:
IapManager.iap_connected.connect(_on_iap_connected)
func _on_iap_connected():
_load_store()
func _load_store():
var skus: Array[String] = ["coins_100", "premium"]
IapManager.load_products(skus)
func _on_products_loaded(products: Array):
update_store_ui(products)
func _on_purchase_completed(purchase: Dictionary):
handle_purchase(purchase)
func update_store_ui(products: Array):
for product in products:
var id = product.id if product is Object else product.get("id", "")
var price = product.display_price if product is Object else product.get("displayPrice", "")
print("Product: ", id, " - ", price)
func handle_purchase(purchase: Dictionary):
var product_id = purchase.get("productId", "")
# Grant purchase to user
pass
Best Practices
Do
- Initialize early: Connect to store as early as possible in app lifecycle
- Handle connection states: Provide feedback to users about connection status
- Use Autoload for persistence: Keep IAP manager as singleton
- Clean up properly: Always remove listeners and end connections
# Good: Using Autoload pattern
func _ready():
if IapManager.is_connected:
load_store()
Don't
- Initialize repeatedly: Don't call init_connection/end_connection for every operation
- Ignore connection state: Don't attempt store operations when disconnected
- Forget cleanup: Always clean up listeners to prevent issues
# Bad: Initializing for every operation
func bad_purchase_flow(product_id: String):
iap.init_connection() # Don't do this
buy_product(product_id)
iap.end_connection() # Don't do this
# Good: Use existing connection
func good_purchase_flow(product_id: String):
if is_connected:
buy_product(product_id)
Purchase Flow Best Practices
Purchase Verification and Security
-
Server-side verification recommended: For production apps, verify purchases on your secure server before granting content.
-
Finish transactions after verification: Always call
finish_transactionorfinish_transaction_dictafter successfully verifying a purchase. -
Never trust client-side data: Always verify purchases server-side before granting premium content.
Purchase State Management
-
Handle all purchase states: Including pending, failed, restored, and cancelled purchases.
-
Handle pending purchases: Some purchases may require approval and remain in pending state.
-
Restore purchases properly: Implement purchase restoration for non-consumable products and subscriptions.
Error Handling and User Experience
-
Implement comprehensive error handling: Provide meaningful feedback for different error scenarios.
-
Graceful degradation: Your app should work even if purchases fail.
-
User feedback: Keep users informed about purchase status.
Testing and Development
-
Test thoroughly: Use real devices and official test accounts.
-
Monitor purchase flow: Log important events for debugging.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Transaction Management Issues
Not finishing transactions:
# Wrong - forgetting to finish transaction
func handle_purchase(purchase: Dictionary):
var verified = await validate_receipt(purchase)
# Missing: finish_transaction call
Always finish transactions after validation:
# Correct - always finish transaction
func handle_purchase(purchase: Dictionary):
var verified = await validate_receipt(purchase)
if verified:
grant_content(purchase.get("productId", ""))
var is_consumable = is_consumable_product(purchase.get("productId", ""))
var result = iap.finish_transaction_dict(purchase, is_consumable)
if result.success:
print("Transaction finished")
Security Issues
Trusting client-side validation:
# Wrong - never trust client-side validation alone
func handle_purchase(purchase: Dictionary):
grant_premium_feature() # Not secure
Always validate server-side:
# Correct - validate on secure server
func handle_purchase(purchase: Dictionary):
var is_valid = await your_api.validate_receipt(purchase)
if is_valid:
grant_premium_feature()
finish_transaction(purchase)
App Lifecycle Issues
Not handling app restarts:
Purchases can complete after app restart, so always check for pending purchases on launch:
# Correct - check for purchases on app launch
func _ready():
_setup_signals()
# After connection established
if iap.init_connection():
check_pending_purchases()
func check_pending_purchases():
var purchases = iap.get_available_purchases()
for purchase in purchases:
await process_purchase(purchase)
Connection Management Issues
Initializing connection repeatedly:
# Wrong - don't initialize for every operation
func purchase_product(sku: String):
iap.init_connection() # Don't do this
buy_product(sku)
iap.end_connection() # Don't do this
Maintain single connection:
# Correct - use existing connection
func purchase_product(sku: String):
if is_connected:
buy_product(sku)
else:
print("Store not connected")
Next Steps
- Review Purchase Implementation Guide for detailed code examples
- Check out Error Handling Guide for debugging tips
- See API Reference for detailed method documentation
